You are here
電子學習平台
2019


Pages
電子學習平台
2019

作為一個可供全球交流的平台,聯合國系統憑藉其通用性、跨學科,以及多界別範疇和角色的特性,一直在全球風險和減災工作上具有特殊的領導地位。
本章節內容涵蓋了由聯合國系統,例如聯合國國際減災策略署 (UNISDR)、聯合國氣候變遷綱要公約 (UNFCCC)、聯合國人類住區規劃署 (UN-Habitat) 及其相關機構,公佈及經我們挑選的文件和指引。
文件的描述來自文件原稿。 這些文件不屬教研中心所有,公眾可在尊重知識產權大前提下使用資料,並必須適當引述出處。
聯合國國際減災策略署修訂的框架和建議
出版物 | 出版年份 | 作者 | 描述 |
 | 2018 | UNISDR | This Strategic Approach to Capacity Development for Implementation of the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction seeks to establish among all stakeholders a common understanding of capacity development within the disaster risk reduction (DRR) context. This Strategic Approach is a resource of empowerment for all relevant capacity development partners and stakeholders, and its goal - A Vision of Risk-Informed Sustainable Development by 2030. |
The Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030
| 2015 | UNISDR | The Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030 (Sendai Framework) is the first major agreement of the post-2015 development agenda, with seven targets and four priorities for action. The Sendai Framework is a 15-year, voluntary, non-binding agreement which recognises that the State has the primary role to reduce disaster risk but that responsibility should be shared with other stakeholders including local government, the private sector and other stakeholders. |
| 2005 | UNISDR | The Hyogo Framework for Action 2005-2015: Building the Resilience of Nations and Communities to Disasters (HFA) is the first plan to explain, describe and detail the work that is required from all different sectors and actors to reduce disaster losses. The HFA is a 10-year plan to make the world safer from natural hazards. |
International Strategy for Disaster Reduction
| 1999 | United Nations | The International Strategy for Disaster Reduction (ISDR) was launched by the Economic and Social Council and endorsed by the General Assembly as an international framework for responding to the challenge presented to the international community by the increasing incidence and scale of disasters. UNISDR was created as an inter-agency secretariat of ISDR together with the Inter-Agency Task Force on Disaster Reduction. |
Yokohama Strategy and Plan of Action for a Safer World
| 1994 | United Nations | The Yokohama Strategy for a Safer World: Guidelines for Natural Disaster Prevention, Preparedness and Mitigation and its Plan of Action was adopted at the 1994 First World Conference on Natural Disaster Reduction, building on the mid-term review of the International Decade for Natural Disaster Reduction. |
International Decade for Natural Disaster Reduction
| 1989 | United Nations | Given the increasing concern about the impact of disasters, the UN General Assembly declared 1990-1999 the International Decade for Natural Disaster Reduction (IDNDR). Initially, IDNDR was influenced largely by scientific and technical interest groups. However, the broader global awareness of the social and economic consequences of disasters caused by natural hazards developed as the decade progressed. |
全球評估報告(Global Assessment Report)減少災害風險
出版物 | 出版年份 | 作者 | 描述 |
| 2019 | UNISDR | This GAR is about understanding better the systemic nature of risk, how we are able to recognize, measure and model risk, and about strategies to enhance the scientific, social and political cooperation needed to move towards systemic risk governance. It reinforces the message that we need to reduce vulnerability and build resilience if we are to reduce risk. It looks at what countries and regional and international organizations have been doing according to formal reporting under the Sendai Framework Monitor (SFM). It also considers country practices in developing national and local plans to enhance risk reduction capacity, to integrate disaster risk reduction (DRR) with development planning and climate change adaptation (CCA), and to pay special attention to risk in rapidly growing cities and fragile/complex contexts. |
| 2017 | UNISDR | The GAR Atlas presents the output of a Global Risk Model (GRM) that can estimate the disaster risk associated with different kinds of hazard faced by national economies throughout the world. The model uses a state-of-the-art probabilistic approach analogous to that applied by the catastrophe modelling and insurance industry over recent decades. This model has been developed by a consortium of leading scientific and technical organisations, under the coordination of UNISDR. |
| 2015 | UNISDR | The fourth edition of the GAR is a resource for understanding and analysing global disaster risk today and in the future. The report explores the large potential losses from disasters currently face by many countries - especially those which can least afford to invest in future resilience and the cost and benefits of disaster risk management (DRM). |
| 2013 | UNISDR | The third edition of the United Nations Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction (GAR) is a resource for understanding and analysing global disaster risk today and in the future. It explores why increasing disaster risks represent a growing problem for the economic and business community at different scales and examines how paradoxically business investments that aimed to strengthen competitiveness and productivity may have inadvertently contributed to increasing risk. |
| 2011 | UNISDR | The second edition of the United Nations Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction is a resource for understanding and analysing global disaster risk today and in the future. Drawing on new and enhanced data, the 2011 report explores trends in disaster risk for each region and for countries with different socioeconomic development. At the same time, over 130 governments are engaged in self-assessments of their progress towards the Hyogo Framework for Action (HFA), contributing to what is now the most complete global overview of national efforts to reduce disaster risk. |
| 2009 | UNISDR | The 2009 Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction (GAR) was launched in Bahrain on May 17, 2009. The Report provides hard-hitting evidence to demonstrate how, where and why disaster risk is increasing globally and presents key findings from a global analysis of disaster risk patterns and trends, including where high mortality and economic loss is concentrated. |
關於氣候變化的框架和建議
出版物 | 出版年份 | 作者 | 描述 |
Paris Agreement under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
| 2016 | United Nations Framework Convention On Climate Change (UNFCCC) | The Paris Agreement is an agreement within the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), dealing with greenhouse-gas-emissions mitigation, adaptation and finance, starting in the year 2020. |
Kyoto Protocol to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
| 1997 | United Nations | The Kyoto Protocol is an international agreement linked to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, which commits its Parties by setting internationally binding emission reduction targets. Recognising that developed countries are principally responsible for the current high levels of GHG emissions in the atmosphere as a result of more than 150 years of industrial activity, the Protocol places a heavier burden on developed nations under the principle of "common but differentiated responsibilities." |
聯合國發展目標
出版物 | 出版年份 | 作者 | 描述 |
| 2015 | United Nations | Sustainable Development Goals are a collection of 17 global goals set by the United Nations General Assembly in 2015. The SDGs are part of Resolution 70/1 of the United Nations General Assembly: "Transforming our World: the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development." The goals are broad and interdependent, yet each has a separate list of targets to achieve. |
| 2000 | United Nations | The Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) were the eight international development goals for the year 2015. Each goal had specific targets and dates for achieving those targets. |
聯合國人類住區規劃署(Habitat)修訂的框架和建議
出版物 | 出版年份 | 作者 | 描述 |
| 2016 | United Nations @Habitat | The New Urban Agenda was adopted at the United Nations Conference on Housing and Sustainable Urban Development (Habitat III) in Quito, Ecuador, on 20 October 2016. The New Urban Agenda represents a shared vision for a better and more sustainable future. If well-planned and well-managed, urbanisation can be a powerful tool for sustainable development for both developing and developed countries. The Habitat agenda is updated every two decades. Past versions can be seen here: Habitat II: The Istanbul Declaration on Human Settlements and the Habitat Agenda (published 1996) Habitat I: The Vancouver Declaration on Human Settlements (published 1976) |
災害期間人道主義救援的參考資料
出版物 | 出版年份 | 作者 | 描述 |
Disaster Response in Asia and the Pacific: A Guide to International Tools and Services
| 2013 | UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA) | Disaster Response in Asia and the Pacific: A Guide to International Tools and Services is designed to help disaster managers in national Governments gain basic knowledge of how to use international tools and services. It aims to support the growing disaster response and disaster response preparedness capabilities that exist at national level across Asia and the Pacific. |
其他有用的工具
出版物 | 出版年份 | 作者 | 描述 |
| 2016 | UNISDR | The UNISDR Terminology aims to promote a common understanding and usage of disaster risk reduction concepts and to assist the disaster risk reduction efforts of authorities, practitioners and the public. |
| 2018 | UN OCHA | The 2018 set includes 295 icons covering topics such as humanitarian clusters, disasters, logistics, security incidents and a user experience/user interface design. |
1: Living with risk: a global review of disaster reduction initiatives. (2004). United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction.
[本文只供英語版本]
[本文只供英語版本]
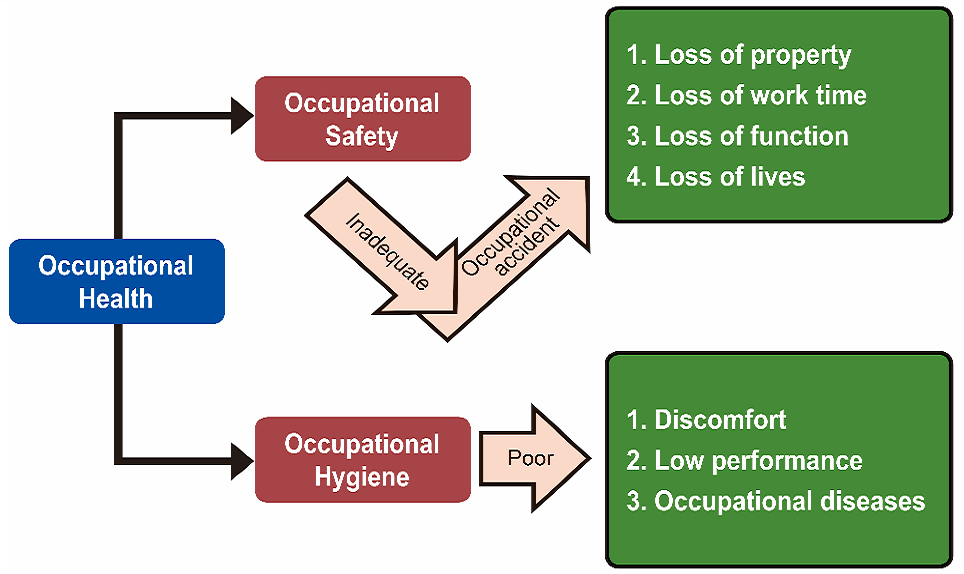
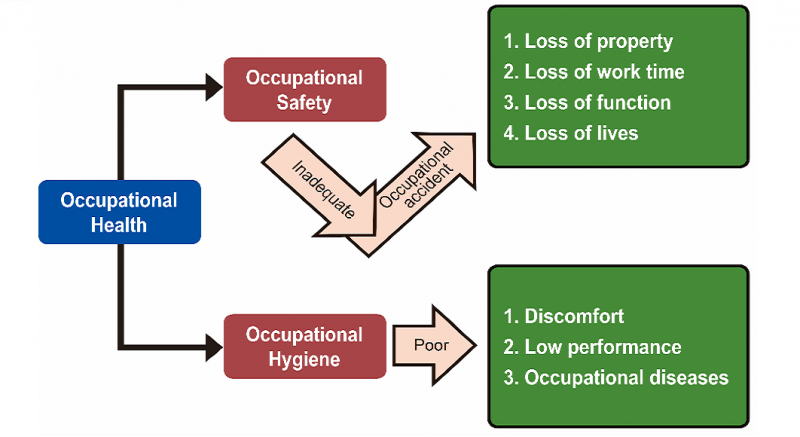
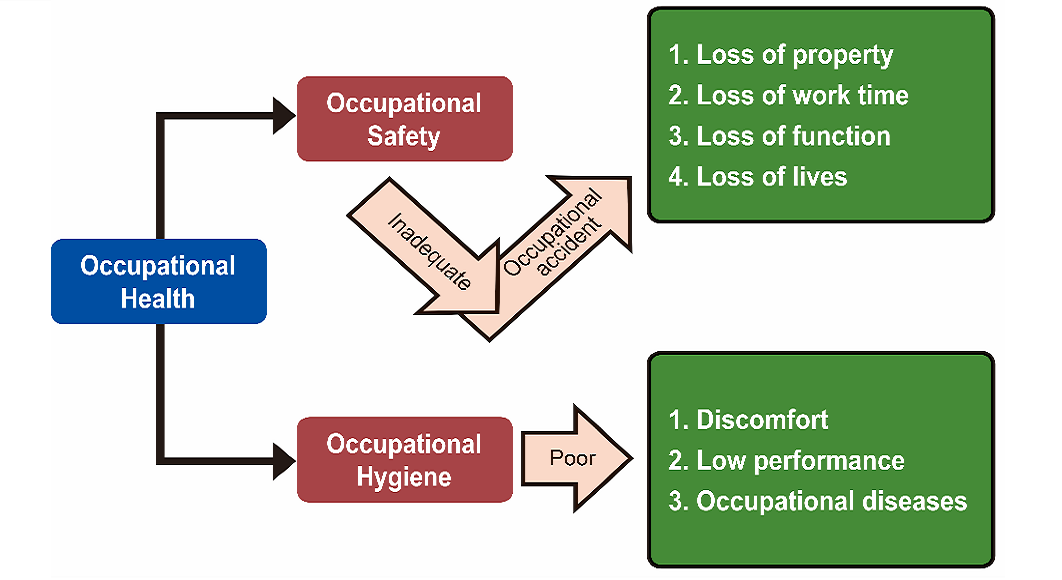
Occupational health is an important topic for health practice. In order to protect health and well-beings, the need to understand the principles of occupational health and prepare for unforeseeable events is rapidly growing. This course will provide the participants with the overview of occupational hazards and health impacts, fundamental of hazards assessment and control. In addition, it will introduce the workplace emergency planning and responses to industrial disasters, as well as the related challenges to occupational health.
To learn more and enroll to the course
[本文只供英語版本。]
(The content of this course is developed by Prof. Shelly Lap-ah Tse, Director of Centre for Occupational and Environmental Health Studies, Jockey Club School of Public Health and Primary, the Chinese University of Hong Kong. The author and her team of tutors (Dr. Feng Wang, Dr. Miaomiao Sun, Miss Suyang Wu) are responsible for the scopes and contents of all lectures included into this course, unless specified elsewhere. The guest editor of this online course is Mr Arick Wan-chung Ng. CCOUC owns the copyright of the diagram and pictures in this course.)
Notes:
The 3rd cohort is now open for registration and study on a first-come-first-served basis. Upon registration, students are allowed to study the course until 31 October 2022 at their own pace. A certificate of completion will be issued for participants who have successfully completed the course.

我們很高興為你介紹一個由香港社會醫學學院及香港賽馬會災難防護應變教研中心 (教研中心) 合辦,並於2019 年 5 月 11 及 18 日舉行為期 1.5 天的災難管理培訓工作坊。這個工作坊是專為於災難防護和應變工作中,負責指揮或管理工作的醫護健康專業人員和相關界別的高級人員而設,目的為向參加者分享實用技能和策略,以改善他們在衞生災害和災難期間的指揮和溝通能力。
各界傳媒人士和企業顧問將會在工作坊中與參加者分享本地的災難處理經驗。請在「下載」的右下方功能表中查看工作坊詳情,重點項目包括:
- 分享和平與戰爭期間的領導經驗 — 梁智鴻醫生
- 山泥傾瀉的災難管理 — 張偉文 博士
- 香港社交媒體狀況及社會聆聽和監察服務的最新消息 — Edmund Lee 先生
- 大數據挖掘及透過近期的重大熱門新聞探討相關例子 — James Leung 先生
工作坊詳情如下:
日期及時間 | 5 月 11 日 (星期六),上午 9:00 – 中午 12:30 |
地點 | 香港仔黃竹坑道 99 號 |
申請辦法 | 請將填妥的申請表格 (可在右方的「下載」功能表中獲取) 電郵至 [email protected] 截止日期:2019 年 4 月 26 日 工作坊名額有限,登記會以先到先得形式安排。 |
| CME | 香港社會醫學學院的參加者將獲得 8 個持續醫學進修學分 (CME)。其他學院的 CME/持續專業發展 (CPD) 學分詳情會在日後公佈。 雖然只出席 5 月 11 日或 5 月 18 日其中一天工作坊的參加者仍可獲得部份 CME 積分,但我們仍鼓勵參加者完成整個為期 1.5 天的工作坊。 |
| 備註 | 工作坊費用全免 2019 年 5 月 18 日的工作坊將提供午膳 |
如有查詢,請發送電郵至 [email protected] 或致電 (852) 2871 8844 與 陳小姐聯絡。

























