You are here
Publications & Research
Publications & Research

Publications & Research
The HKJCDPRI Publications Section contains collaborative researches and publications with our partners and renowned academic institutions, and other research and development projects related to disaster preparedness and response.
The Guidelines section contains our selected collection of technical information, operational guidelines and useful tools for disaster management.
The Blog sub-section provides a platform where our team and peers share news and updates, as well as opinions and experiences in building disaster preparedness for the communities.
The blog posts are written by the author in his own personal capacity / affiliation stated. The views, thoughts and opinions expressed in the post belong solely to the author and does not necessarily represent those of Hong Kong Jockey Club Disaster Preparedness and Response Institute.
All resources listed here are freely and publicly available, unless specified otherwise. We ask users to use them with respect and credit the authors as appropriate.
2022

[本文只供英語版本]
[本文只供英語版本]
Abstract
This article focuses on children's participation in disaster risk reduction. It draws on a 2018 study done in New Zealand with 33 school children who conducted participatory mapping with LEGO and the video game Minecraft to assess disaster risk in their locality and identify ways to be more prepared. The research involved participatory activities with the children actively involved in the co-design, implementation, and evaluation of the initiative. A focus group discussion was also conducted to assess the project from the viewpoint of the schoolteachers. The results indicate that LEGO and Minecraft are playful tools for children to participate in disaster risk reduction. The research identifies four key elements of genuine children’s participation, including the Participants, Play, the Process, and Power (4 Ps). This framework emphasizes that fostering children's participation in disaster risk reduction requires focusing on the process through which children gain power to influence decisions that matter to them. The process, through play, is child-centered and fosters ownership. The article concludes that Play is essential to ground participation within children’s worldviews and their networks of friends and relatives.
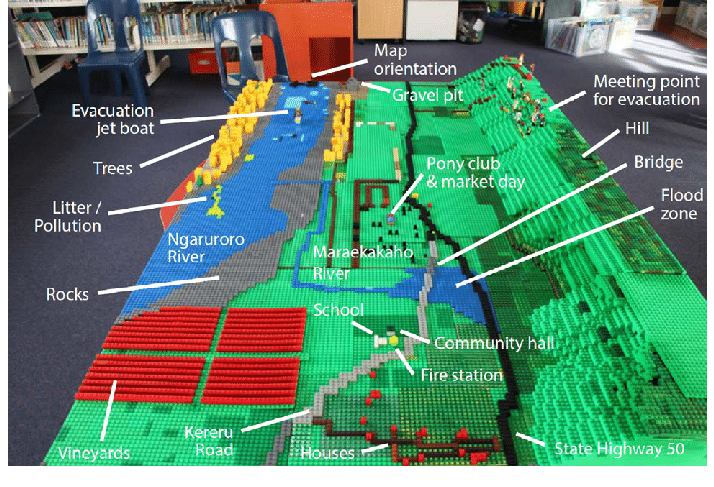
LEGO map of Maraekakaho village produced by the children in the disaster risk reduction participatory mapping project, New Zealand 2018
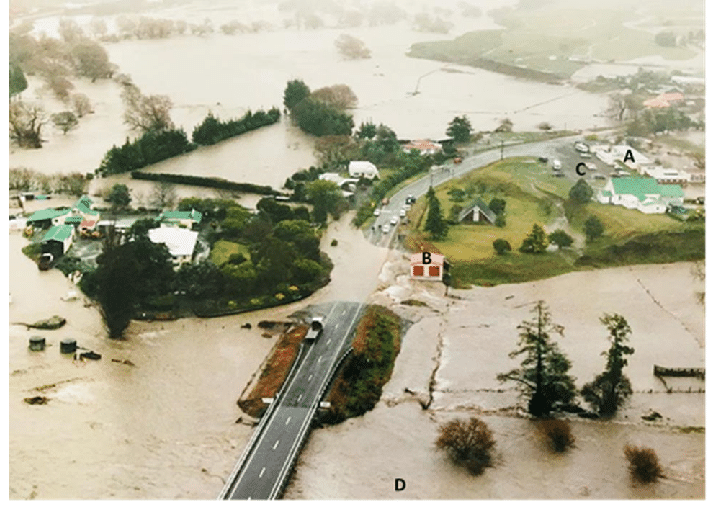

Maraekakaho village on the Maraekakaho and Ngaruroro Rivers, North Island, New Zealand.
Maraekakaho flood in 2007. A: Maraekakaho School; B: Original location of the fire station; C: New fire station location; D: Maraekakaho River (rubbish station located to the south, just out of frame).
Photograph by one of the community members from Maraekakaho, with permission for publication

[本文只供英語版本]
[本文只供英語版本]
This article originates from Monash University https://www.monash.edu/medicine/news/latest/2022-articles/rapid-dna-technology-set-to-speed-up-disaster-victim-identification
30 June 2022
Disaster Victim Identification (DVI) is a vital task undertaken by forensic teams after mass-casualty incidents. It involves comparing DNA from deceased persons with that of living relatives and looking for kinship. Identifying victims accurately and quickly is important for families not just for emotional closure, but to help them navigate a complex web of urgent legal and administrative tasks that may free up access to badly needed finances and support.
Researchers from the Victorian Institute of Forensic Medicine (VIFM) and the Monash Department of Forensic Medicine (DoFM) have recently written this expert review of a long-awaited emerging technology that may vastly speed up the process, and enable in-field DNA analysis – Rapid DNA. This could greatly benefit people experiencing large-scale disasters that overwhelm the local authority’s ability to respond, and may have a role in crime scene investigation and other activities.
Traditional DNA analysis involves many pinch points where time is lost. Samples must be transported to an accredited laboratory, case processing backlogs slow things down, and reporting pipelines back up as qualified staff are caught up in processing. A number of improvements have been made over the years, such as automation of the laboratory processes, reduction in reaction times of DNA tests, and software assisted interpretation of DNA profiles. Whilst valuable, none of these change the fundamental processing pipeline itself.
First author Zoe Bowman is a Monash PhD student working clinically at VIFM. She says, “Members of our team assisted with DVI during the Indian Ocean Tsunami in 2004, and the Victorian Black Saturday fires of 2009. I think its fair to say that we, along with many other forensic identification teams around the world, have been waiting somewhat impatiently for a new technology that would allow for DNA profiling in the field.
“Now it’s here, it’s important it is thoroughly validated in a variety of scenarios.”
Rapid DNA has been facilitated by the miniaturization of DNA testing technology through microfluidics, and the development of specialized instrumentation. The new, portable devices encapsulate the entire workflow, and could potentially allow non-experts to conduct sample testing in under two hours.
“These are kind of like plug-and-play devices. You insert your sample swab along with a test card which contains all the chemicals needed for the test, and the result comes out. The user experience is really quite simple. But there is an astounding amount of technology underpinning that.”
While there are three commercially available Rapid DNA devices on the market, the decision to deploy them is still not straightforward. Traditional laboratory-based DNA profiling has been well established as a reliable and robust technique, much like laboratory PCR tests for COVID-19. The use of Rapid DNA technology is somewhat comparable to the use of rapid antigen test for COVID-19.
“To choose Rapid DNA over lab-based options, you’d need to consider exactly how the results will be used. Is this going to end up in a court of law? In which case, courts may not accept DNA results generated outside an accredited laboratory. Are speed and logistical ease more important to you than quality and cost per test? They might well be in a disaster scenario, but maybe less so in a routine crime scene investigation.”
There are also some unknowns with regards to contaminants in samples that may impede the analysis. Most Rapid DNA devices are designed to use mouth swabs. Recent use of tobacco or coffee by the sample donor may cause difficulties. However, most studies to date indicate the effects are within acceptable limits in disaster scenarios.
What is less well studied is interference caused by decomposition of DNA over time, which may become a problem in disasters involving significant delay until victims are found, or in warm climates. The impact of chemicals often found at disaster sites – such as aviation fuel or fire-retardant chemicals at plane crash sites – is also largely unknown at this stage.
The flip side of sample collection from deceased disaster victims is the collection of samples from living people searching for missing loved ones.
Zoe says, “A recent example of this is the 2018 Camp Fire disaster in California, which killed 85 civilians. Rapid DNA was successfully deployed in the field at family centres, fast-tracking familial sampling and releasing laboratory staff to focus on more complex post-mortem samples.”
Beyond DVI, the technology has a range of potential applications. In crime investigations, a person of interest could be swabbed and profiled on arrest, with rapid database matching enabling arresting officers to link the person with other crimes whilst in custody. The technology may also have a role in immigration, military applications, missing persons investigations and mass grave discovery.
However, there are potential complexities that will need to be addressed. The presence of miniscule amounts of DNA, degradation over time, and DNA from multiple sources – human and animal – provide challenges for crime scene investigations, as does the likely lack of trained staff with the ability to assess sample suitability. Mass graves are often found in resource poor areas with limited laboratory support. Rapid DNA technology could overcome this, but improvements in analysing degraded skeletal DNA are likely needed before the technology is widely embraced for this purpose.
Last author A/Prof Dadna Hartman says, “There is still a long way to go in terms of testing this technology and ensuring it is fit-for-purpose in many different scenarios. But I’m very optimistic that these will be overcome in due course, and this will be a very powerful tool that will bring faster closure and support to devastated families around the world.”

[本文只供英語版本]
[本文只供英語版本]
Highlights
- •
Increasing disaster risks require universities to consider their resilience capacity.
- •
A complex array of strategies is required, including transformational changes.
- •
A framework is proposed to guide university development of resilience strategies.
Abstract
Recent years have provided stark insights into the challenges of dealing with multiple, overlapping disasters in many parts of the world. Climate change reports indicate that these severe and complex disaster scenarios are likely to become more frequent. This paper provides a reflective oversight of the changing roles of universities in the context of these new disaster risk scenarios. A transformative approach is encouraged as part of an array of resilience strategies, interconnected systemically and temporally. A framework for disaster resilient universities is proposed based on the literature relating to the different spheres of university responsibilities and respective stakeholder groups, with due consideration for underlying principles and social responsibilities for disaster resilience.
Click for Full Report






